MGMT 17300: Data Mining Lab
Intro. & Technical Enablers
August 01, 2024
Welcome!
Overview
- Introductions
- Course Overview and Logistics
- Motivation
- Course Objectives
- Key Topics
- M3DM and other approaches.
- Key terms.
- M3DM three technical pillars.
- M3DM and other approaches.
Introductions
Instructor
- Clinical Assistant Professor in the Management Department at Purdue University;
- My academic work addresses Political Communication, Data Science, Text as Data, Artificial Intelligence, and Comparative Politics.
Instructor’s Passions


Instructor’s Passions

Students
- It is your turn! - 5 minutes
- Present yourself to your left/right colleague and tell her/him what are the current two main passions in your life.
Course Overview and Logistics
Course Overview and Logistics
Materials:
Brightspace
Modern Data Driven Decision Making - Text Book

Motivation
What motivated you to enroll in the Data Mining Lab course?
Motivation
“Without data, you’re just another person with an opinion.” – W. Edwards Deming
Study Design
Study Design
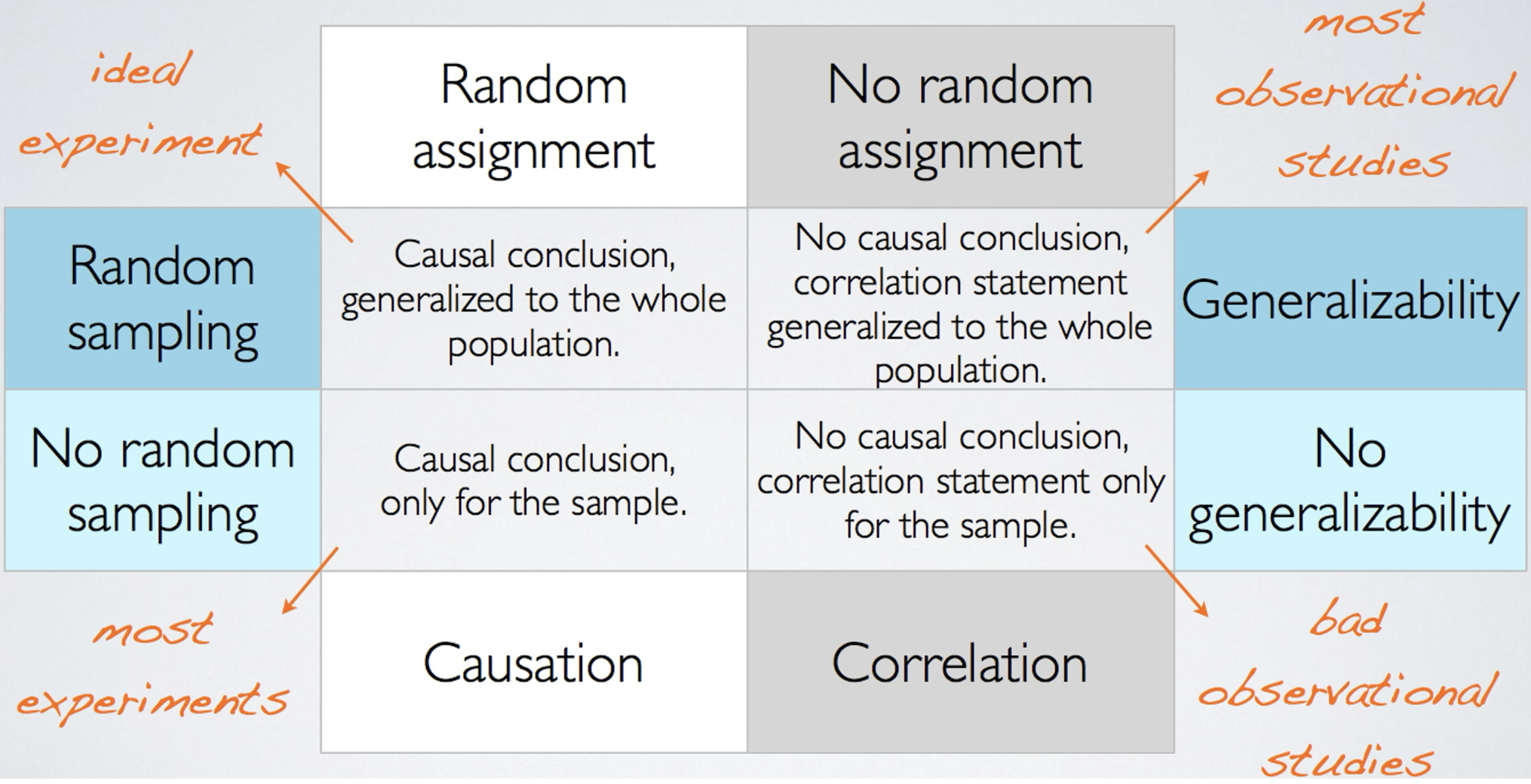
Observational
In observational studies, no attempt is made to control or influence the variables of interest. A survey is a good example.
An example of an observational study is researchers observing a randomly selected group of customers that enter a Walmart Supercenter to collect data on variables such as time spent in the store, gender of the customer, and the amount spent.
Experimental
An experimental study involves the active manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for confounding factors. Participants are typically randomly assigned to groups (e.g., treatment vs. control), and outcomes are compared to determine causal relationships. This design provides strong evidence for cause-and-effect due to the controlled environment and random assignment.
The largest experimental study ever conducted is believed to be the 1954 Public Health Service experiment for the Salk polio vaccine. Nearly two million U.S. children (grades 1 through 3) were selected.
Study Design

Study Design: Random Assignment vs. Random Sampling
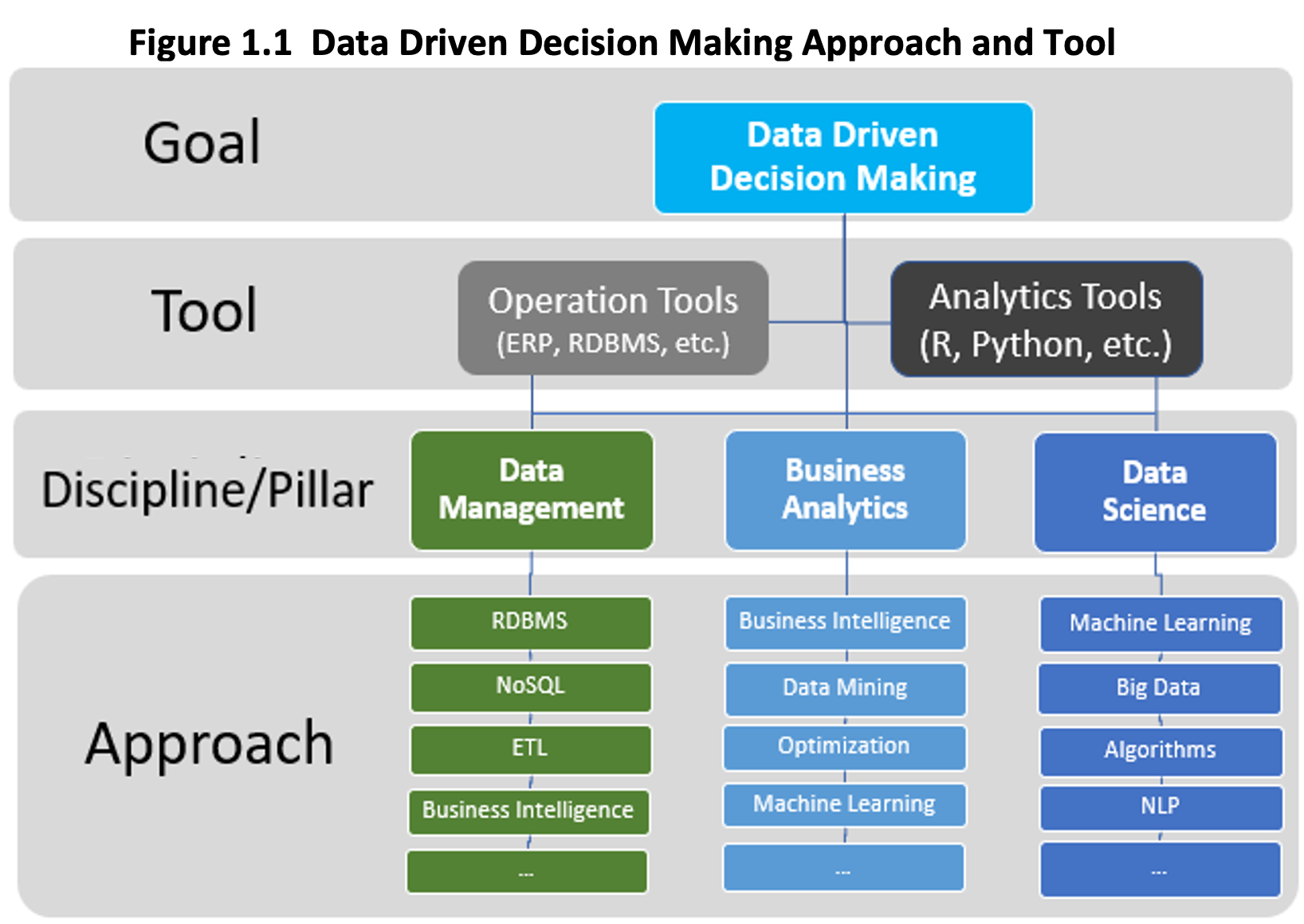
Modern Data Driven Decision Making
Text Book

Modern Data Driven Decision Making
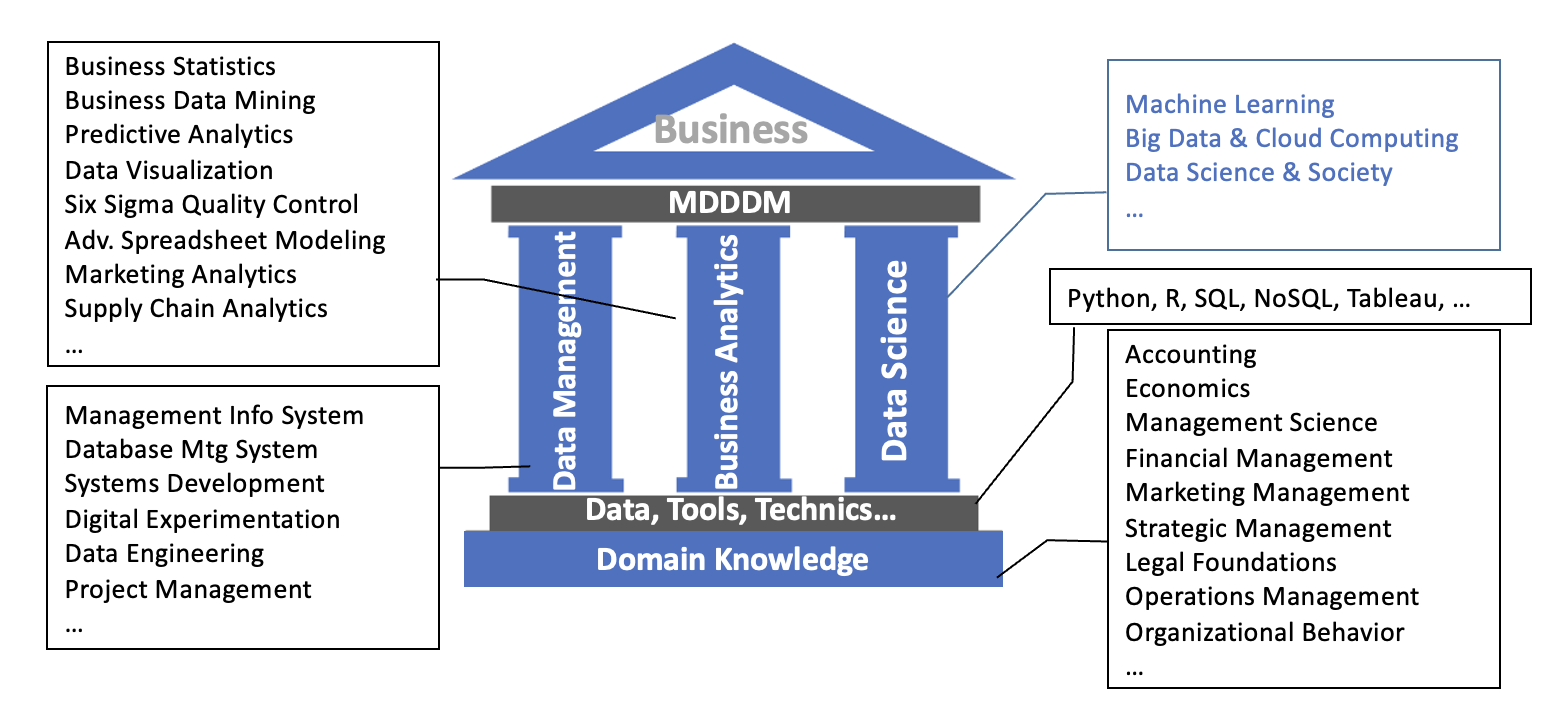
Modern Data Driven Decision Making
Statistical Inference
Statistical Inference
Population: the set of all elements of interest in a particular study.
Sample: a subset of the population.
Descriptive Statistics: Tabular, graphical, and numerical summaries of data.
Inferential Statistics: The process of using data from the sample to make estimates or test hypotheses about the characteristics of a population
Estimation: Using sample data to approximate population parameters.
Hypotheses Testing: Determining if there is enough evidence in a sample to support a claim about a population.
Prediction: Forecasting future events based on historical data.
Summarizing and Presenting Data
Summarizing and Presenting Data
Summarizing and Presenting Data

Data Science, Big Data, and Data Mining
Data Science, Big Data, and Data Mining - Definitions
- Data Science:
- The interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data.
- Big Data:
- Extremely large datasets that may be analyzed computationally to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, especially relating to human behavior and interactions.
- Data Mining:
- The practice of examining large databases to generate new information, involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems.
How Data Science, Big Data, and Data Mining are Used
- Data Science:
- Personalizing marketing efforts by analyzing customer data to predict preferences and buying behavior.
- Optimizing supply chain management through predictive analytics.
- Big Data:
- Analyzing customer feedback and social media interactions to improve customer service and develop new products.
- Enhancing risk management in financial institutions by monitoring transaction patterns and detecting fraudulent activities.
- Data Mining:
- Identifying potential leads and sales opportunities by analyzing past sales data and customer demographics.
- Enhancing customer retention by understanding churn patterns and developing targeted retention strategies.
Summary
Summary
Modern Data Driven Decision Making (M3DM):
- M3DM is essential in leveraging data to guide business decisions.
- The approach integrates statistics, machine learning, and data management to inform and optimize strategies.
Technical Pillars:
- Data Acquisition: Gathering relevant and high-quality data.
- Data Processing: Cleaning, transforming, and organizing data for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Using statistical and machine learning techniques to extract insights.
Practical Application:
- Real-world applications of M3DM include predictive analytics, customer segmentation, and operational optimization.
- Data-driven decisions can significantly enhance business performance and competitive advantage.
Thank you!
Data Mining Lab
